According to some, profit is the entire reason for business to exist.
Profit refers to the amount of money a business keeps from its sales after all costs are accounted for. There are different ways to measure it, but it essentially refers to the money that a business owner keeps or earns from the business.

What is profit
What is profit, exactly?
According to conventional accounting, also known as generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), there are different ways of measuring profit.
When investors and business owners talk about profit, they are typically talking about net profit, also known as net income. This is the bottom-line measurement of profit, the figure at the bottom of an income statement.
It measures profit after all costs are included such as cost of goods sold, operating costs like selling, general, and administrative expenses, interest expense, and income tax.
There are other measures of profit further up the income statement, such as pre-tax profit, operating profit, and gross profit, which account for only some of those cost items.
Why is profit important?
Why is profit important?
Profit is important for both businesses and investors since this is the money that a business earns and the amount that investors have a claim on.
There are other key metrics that investors use to track the performance of a business, including revenue, which measures top-line sales, and cash flow, which measures cash profits.
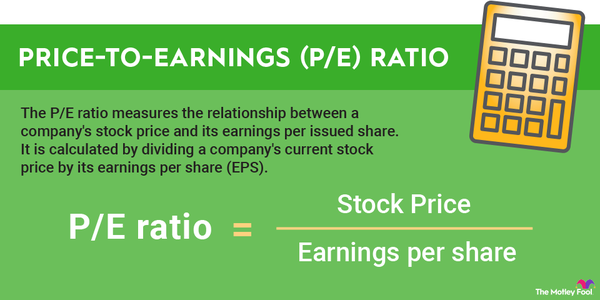
However, profit, or net income, is generally seen as the metric that best reflects the underlying strength and profitability of a business. It's also important because earnings -- another word for profits -- are typically used by investors to measure valuation, using the price-to-earnings ratio. This metric divides the price per share of a stock by its earnings per share, telling you how much profit each share of the stock entitles you to.
If a stock pays dividends, those dividends are paid out of profits so it's important for dividend investors to understand how the quarterly dividend compares to quarterly profits, which is known is the dividend payout ratio. If the dividend exceeds profits, it could be at risk of a cut.
How to analyze profits
How to analyze profits
Profit is one of the most useful figures for investors. There are different profit metrics that you can use to guide your investments.
First, the price-to-earnings ratio is often the best way to determine how cheap or expensive a stock is. You can also easily compare the P/E ratio of two companies with each other to see which one is cheaper. While that won't tell you everything about the two stocks, valuation is one key point you should consider.
Additionally, you can compare profit margins between businesses and industries. Some industries generate high profit margins, including the tech and healthcare sectors. When you look at profit margin, it's important to compare two companies within the same industry, or to understand that some industries have wider profit margins than others.
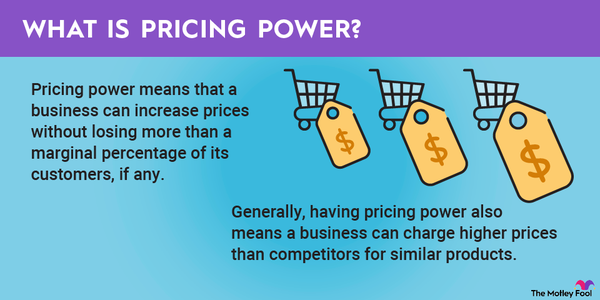
Finally, looking at profits higher up on the income statement can also be informative. Gross profit margin, for example, can be a good indicator of strength. In the semiconductor industry, gross margin is a good representation of pricing power and relative strength to competitors. It also shows how much money a company has to invest after they've paid for their products.
Related investing topics
Example
An example of profit
Let's say you have a restaurant where you generate $1 million a year in revenue.
You spend 70% of that money on direct costs like food, labor, rent, and paper products. Your costs of goods sold would be $700,000 and your gross profit would be $300,000.
You spend $200,000 on overhead like management salaries, insurance, technology, and other costs that are directly making the restaurant run. That would leave with $100,000 in operating profit, or 10% of revenue. Finally, the business pays taxes of 20% of operating profit, or $20,000, leaving it with $80,000 in net profit, or net income.
While $80,000 is the bottom-line profit figure, it's important to understand how profit works at every level of the income statement.