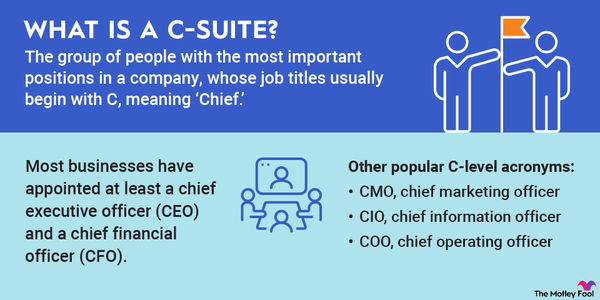
The C-Suite of a company features the individuals who have the most important roles in the daily operations of the business. When the organization is responsible for or controls investment portfolios, this group of high-level executives should include a chief investment officer. The role of a chief investment officer (CIO) is wide ranging, but crucial to ensure that the business makes wise investments and upholds its corporate obligations to shareholders.
Read on to learn what a chief investment officer is, what this role entails, why investors should care, and more.

Overview
What is a chief investment officer?
The chief investment officer manages a company's investment activities, as well as its overall investment strategy. This job may involve numerous functions depending on the nature of the individual role and the size and scale of the organization. Any company with a portfolio of assets -- which may include private equity investments, public equity investments like stocks, real estate, and fixed-income assets, to name several examples -- may need a chief investment officer. Companies involved in the finance, insurance, and banking sectors all typically have a chief investment officer serving in the C-suite.
Multinational conglomerates, universities, nonprofit organizations and other companies that control investments in tangible or intangible assets will also usually have a chief investment officer. The individuals who occupy these roles typically have an extensive background in finance and economics. The chief investment officer must manage challenges in the public and private markets while leveraging effective solutions to successfully manage the risks and returns of the company's investments.
Why they are important
Why is a chief investment officer important?
The role of a chief investment officer is important in numerous types of public and private organizations because this person handles a variety of aspects associated with portfolio management. This can entail actively researching and selecting the investments of the company or delegating these actions to a team of investment managers whom they oversee but who make day-to-day portfolio decisions.
The chief investment officer is responsible for establishing the company's investment processes, making investment recommendations, selecting members of the asset management team, and overseeing the allocation of assets to build the company's wealth and profitability with time. This individual must have extensive knowledge of all asset classes and investment products, as well as optimal return generation strategies.
The chief investment officer must oversee capital allocation towards investment activity that moderates risk exposure while maximizing profits for stakeholders. Although the chief investment officer's asset allocation strategy may adhere to guidelines established by the board of directors, this role may also be the ultimate arbiter of striking a balance between an aggressive or conservative strategy for the entity. A company's chief investment officer should be an effective communicator with strong leadership abilities and analytical skills.
How a CIO affects shareholders
How does a chief investment officer affect shareholders?
Because a chief investment officer's job is to grow returns on a company's investments while actively managing risk, this role has a direct impact on the value of the returns that the organization's shareholders enjoy. Chief investment officers must uphold their duty to the board of directors and shareholders through all market cycles while ensuring the financial health of the organization and ensuring that investment maneuvers do not undermine the company's liquidity or day-to-day functions.
A chief investment officer should be able to effectively maximize returns from investments and manage associated risks while tracking and adjusting the investment portfolio to maximize profitability. Moreover, the chief investment officer will keep shareholders updated on how investments are performing while staying apprised of market trends, economic shifts, and regulatory changes that will impact the organization's asset allocation strategy.
Well-known CIOs
Who are some of the most well-known chief investment officers?
There are plenty of prominent real-world examples of chief investment officers who have been indispensable to the growth of their respective organizations and delivering enviable shareholder returns. One of the most well-known individuals who has inhabited the role of both chief executive officer and investment manager is the Oracle of Omaha, Warren Buffett. Under his leadership, holding company Berkshire Hathaway (BRK.A -0.71%)(BRK.B -0.47%) has delivered steady shareholder returns through economic thick and thin with stakes in value-oriented enterprises ranging from financial stocks to tech stocks to healthcare stocks to consumer staples stocks.
Over the trailing-10-year period, the company has delivered a total return around 220% to shareholders, only slightly behind the overall return of that S&P 500 during the same period. Buffett's lieutenants Ted Weschler and Todd Combs (who is also the CEO of GEICO) serve as investment managers, and both are rumored to be in line to take over the chief investment officer role for Buffett in the future.
Related investing topics
Another high-profile example of a chief investment officer is the founder and CEO of Ark Investment Management, Cathie Wood. The firm is known for its exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that are focused on high-growth, technology-centric companies. Its flagship fund is the ARK Innovative ETF (NYSE:ARKK). Where Buffett focuses on blue chip investments with strong profitability, cash flows, and more predictable returns, Wood prefers innovative companies in high-growth, emerging industries like artificial intelligence, blockchain technology, and robotics.
These transformative industries may carry the potential for higher returns while also inherently carrying higher levels of risk. When you're investing in a company or fund with a chief investment officer at the helm, understanding their strategy is one aspect of gauging whether the organization's investment style aligns with the personal risk tolerance level you've set for your portfolio. No two investment strategies are exactly the same, and different approaches can be effective over the long run.